animal models
At Cilcare, we are dedicated to advancing the field of auditory research by offering a wide range of validated in vivo models that facilitate the comprehensive assessment of hearing disorders, sensorineural hearing loss, tinnitus, ear inflammation, and auditory neuropathy comorbidities associated with chronic neuro-inflammatory diseases. Our expertise in preclinical research spans across a diverse spectrum of auditory conditions, and we take pride in providing the scientific community with cutting-edge tools and solutions to address complex challenges in auditory health. Whether you are exploring the intricacies of hearing impairment, the underlying mechanisms of tinnitus, or the association between hearing loss and Diabetes or Parkinson’s Disease, we are here to empower your research and innovation.
noise-induced hearing loss and synaptopathy
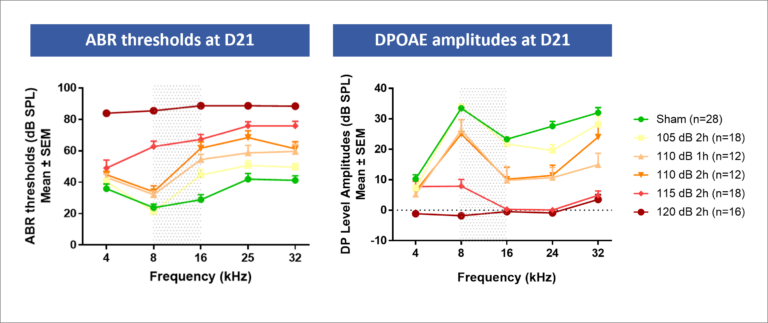
Noise trauma can result in 2 types of injuries to the inner ear depending on the intensity and duration of the exposure: a temporary threshold shift (TTS) that returns to normal, inducing synaptopathy, or a permanent threshold shift (PTS) leading to irreversible hearing loss. CILcare’s models are relevant for testing drug candidates, cell and gene therapies involved in oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, cell growth, synaptopathy, neurotrophy and regeneration on auditory dysfunction or hair cell damage.
- Noise-induced permanent hearing loss (PTS)
- Noise-induced synaptopathy and transient hearing loss (TTS)
- Rat, mouse, guinea pig models
- Protection & regeneration protocols
- Functional read-outs: ABR, DPOAE, Wave I analysis
- Histopathology: cochleogram (hair cell count), ribbon synapses count, SGN, and fiber count
- RNA & protein arrays
Progressive hearing loss demonstrated with trauma intensity’s variation
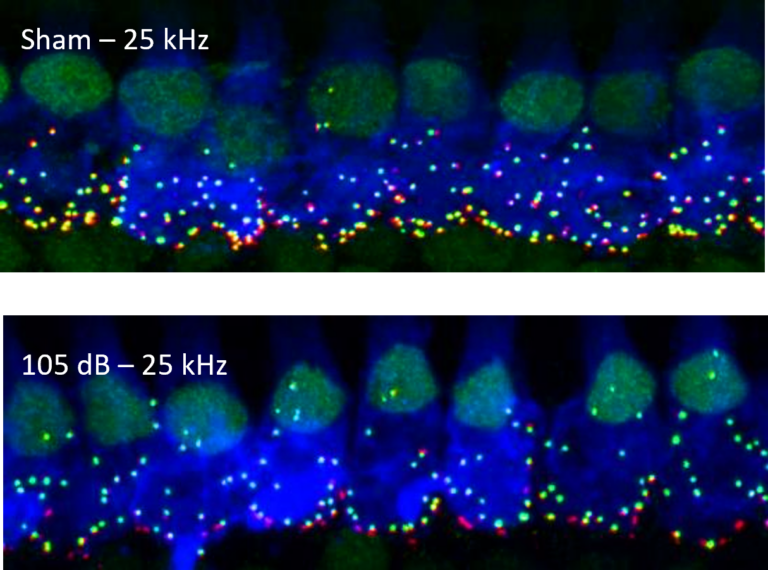
Ribbon synapses count in a 105 dB traumatized rat model
cisplatin & antibiotic-induced ototoxicity
Ototoxicity may be defined as the property of certain therapeutic agents and other chemical substances to cause functional impairment and cellular degeneration of the tissues of the inner ear. More than 200 compounds are listed as ototoxic, including cisplatin, which is still vastly used in chemotherapy in pediatric populations, and aminoglycosides, used in treatment of some infectious diseases.
Whether you are looking to establish a first proof of concept in hearing indication or evaluate the long-term effect of a compound in a protocol that mirrors real-world clinical administration, Cilcare’s robust and validated models represent an initial successful step towards the therapeutic intervention of hearing disorders.
- Ototoxic insult with cisplatin, antibiotics (gentamicin, etc.)
- Acute and chronic models in rats, guinea pigs, and mice
- Available positive control
- Read-outs: ABR, DPOAE
- Histology: Cochleogram
- Blood sampling: compound interaction
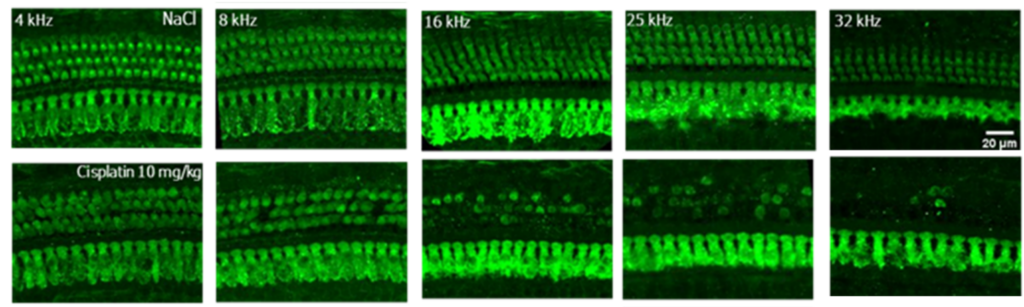
Representative immunostaining images showing hair cell loss at 16, 25 & 32 kHz after cisplatin administration in rats
salicylate-induced tinnitus
Tinnitus is the perception of a phantom sound without a corresponding external sound source which, in most cases, occurs with hearing loss. The physiopathology of tinnitus is caused by abnormalities in the inner ear and dysfunctions of the central nervous system.
Cilcare’s tinnitus model enables short in vivo studies with a relatively low variability. Salicylate, a common tinnitus-inducing agent, metabolizes within hours to days, providing the ability to monitor physiological changes before, during, and after tinnitus induction.
- Acute rat model
- Primary endpoint: GPIAS
- Additional read-outs: Hyperacusis, electrophysiology
- Imaging: MEMRI
- Biochemical biomarkers
ouabain-induced auditory neuropathy
Auditory neuropathy is a complex auditory disorder characterized by impaired transmission of sound from the inner ear to the brain. This condition results from damage to the auditory nerve, which connects the sensory hair cells in the inner ear to the brainstem. Unlike other types of hearing loss, auditory neuropathy primarily affects the neural aspects of hearing, leading to difficulties in processing sound and understanding speech.
Contact us to to know more about this model.
other disease & transgenic models
Cilcare specializes in characterizing the hearing functions of your transgenic animal or specific pathological animal models, delivering robust auditory data.
From functional hearing assessments to comprehensive post-mortem samplings and histopathology assessment, we offer a complete solution to get your model phenotyped.
Contact us to know more about our these models.
rodent & large species
We have the capabilities to work on a diverse range of rodent and large species, including pregnant females and transgenic mice.