screening / dose selection for ototoxicity or otoprotection
ex vivo assay on cochlear explants
Cochlear explant studies offer a valuable bridge between in vitro investigations and full-scale in vivo experiments. By focusing on isolated cochlear tissue, we gain crucial insight into the efficiency and mechanism of action of drug candidates or gene therapy. This meticulous approach allows for rigorous dose selection and optimization before advancing to live animal models, ultimately saving time and resources while enhancing the prospects of successful auditory restoration or absence of ototoxicity.
Immunostaining of a cochlear whole mount from rat
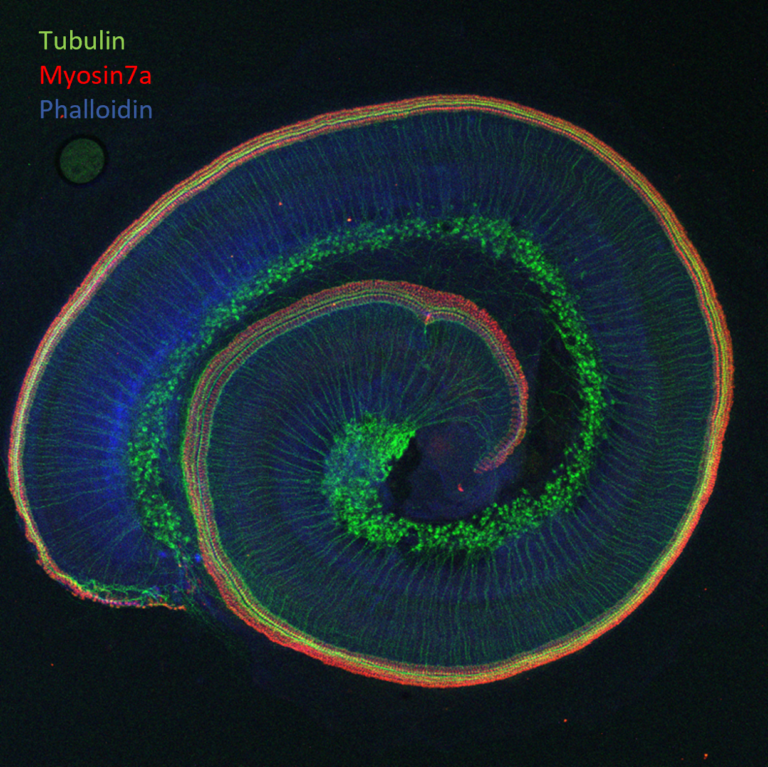
Cilcare’s cochlear explant models allow to quantify and qualify damage to crucial cochlear structures, including outer and inner hair cells, supporting cells, ribbon synapses, and spiral ganglion neurons. Acquisition is performed according to the cochlear tonotopy: base, median, and apex.
- Ototoxicity model: Insult with cisplatin, gentamicin, etc.
- Excitotoxicity model: Insult with NMDA/Kainate
- Histology: Staining of Hair cells, Supporting cells, Auditory Fibers, Stereociliae, Ribbon Synapses, and Spiral Ganglion Neurons (Myosin7a, SOX2, Phalloidin, Tubulin, CtBP2, GluR2, Homer, NF5)
- Read-outs: hair cell count, hair cell organization scoring, pre- and postsynaptic markers counting, neurofilament, SGN counting
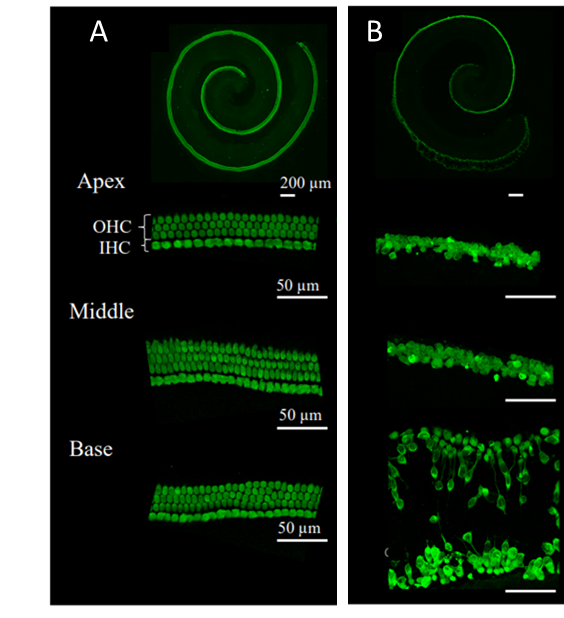
Hair cells labelled with Myosin7a: sham (A) and treated with cisplatin (B)
Discover our in vitro model and our zebrafish model.